Passwordless Authentication for Consumers
Today’s digital world demands both security and convenience, a balance that traditional password-based authentication often struggles to achieve. Enter passwordless authentication—a seamless yet secure access method that frees users from the complexity of password management. This approach not only simplifies the login process but significantly enhances security, making it an increasingly popular choice among consumers. Unlike enterprise environments, where authentication flows and challenges can be more intricate due to regulatory, scalability, and security requirements, consumer-focused passwordless solutions prioritize user experience without compromising on security. In this post, we’ll explore the various passwordless authentication options available to consumers, underscoring their benefits and potential drawbacks.

Magic Links:
Just what is a magic link? A magic link is a unique, one-time-use URL sent to the user’s email address. When the user clicks on this link, they are automatically logged into the application or service. This method relies on the security of the user’s email account and eliminates the need for remembering passwords.
How do magic links works? The user enters their email address on the login page. The service sends an email containing a magic link. The user clicks the link, which verifies their identity and grants access.
What are good use cases for magic links? Subscription services, web applications, and any service looking to streamline login processes.
What are the downsides of magic links? Using magic links is convenient, however, it is making an assumption that your email is 100% secure. For many consumers, this is not always the case. If someone else has access to your computer, smartphone or tablet, they likely can log into your accounts as you.
In todays world, it is critical that you have secured your email account as much as possible. If you have a Gmail, Outlook.com, Apple or any of the mainstream email accounts, you should have multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled on them. You should routinely check to see where your account is currently logged in at. It is possible for your account to be logged into an attackers computer and you not even realize it.
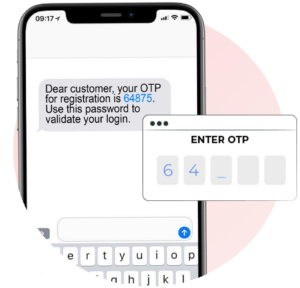
SMS OTP Codes:
What is an OTP Code? An SMS One-Time Password (OTP) is a code sent to the user’s mobile phone via text message. The user enters this code on the login page to gain access. This method uses something the user has (their phone) as an authentication factor.
How do OTP Codes work? If you are a new user to a service, you are asked for your mobile phone number. If you are an existing user with an account, the mobile phone number you originally registered to your account is used. Upon requesting to log in, you receive a text message with an OTP, which they enter on the website or app to authenticate. These codes are typically 6-8 characters long. Most websites utilize numbers only, some will generate codes that have numbers and letters.
What are good use cases for SMS OTP Codes? Banking, online shopping, and any service requiring an additional layer of security beyond just a username.
What are the downsides of SMS OTP Codes? Generally, SMS OTP codes are not considered to be secure as SMS messages themselves are not encrypted and can easily be redirected, intercepted and stolen. The use of SMS OTP codes provides a false sense of security and often times leads to people falling victim to phishing attacks where they give the OTP code to a malicious actor. SMS OTP codes are more secure than using just a password, however, it is recommended to implement a more secure method of authentication. Phishing-Resistant authenticators such as FIDO2 keys or Push Notification with Number Matching are much more secure.
Many sites, including banking platforms, are still utilizing SMS OTP codes. If this is the only option you have for your banking site, you should utilize this. If you are given the option for an app based MFA code, such as that Google Authenticator app, this would be a more secure option.
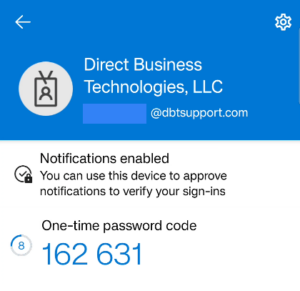
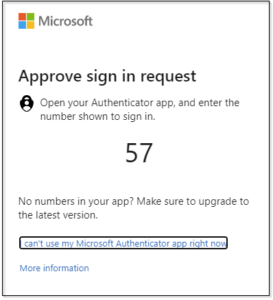
Authenticator Apps:
What are authenticator apps? Authenticator apps generate time-limited OTPs, providing a more secure alternative to SMS OTPs. The app, installed on your device, generates a new code every 30 seconds. Some platforms such as Google, Microsoft, Facebook and various banks to name a few, also use their authenticator app to send a push notification to confirm authentication requests.
How do Authenticator Apps Work? To enable the rotating OTP codes in your authenticator app, you link your account to the authenticator app by scanning a QR code. To log in, you open the app to get a new OTP and enter it on the login page. For push-based notifications, sites that support push notifications will send you an automatic push notification to your mobile app. For example, if you are logged into your Facebook mobile app and you attempt to log into Facebook on a computer, the Facebook app will send a push notification to your phone asking if you just tried to log in. If you approve, you will be logged into Facebook on the computer web browser.
What are good use cases for Authenticator Apps? Online accounts requiring strong security, such as email, cloud storage, social media, and financial services. Outside of FIDO2 Keys/PassKeys (Discussed below), you should use authenticator apps where possible.
What are the downsides to authenticator apps? For some, the initial setup is not as easy. Those that are less tech savvy do not always understand how to scan the QR code, then how to enter in the number that is changing regularly. Your ability to authenticate to a website is also dependent upon you having your device. If your device loses power, is lost/forgotten/stolen, or you trade your device in to get a new one, you may not be able to log back into your account again. Recovering your account in the event that your mobile authenticator is lost can be cumbersome.
Additionally, mobile authenticator apps that do not support number matching are susceptible to phishing attacks. If a malicious actor attempts to log into your account and you approve the push notification and there is no second form of check, such as number matching, the malicious actor will be logged into your account.
Mobile authenticators provide a great level of security and help prevent a significant number of attacks. We strongly recommend that you implement Mobile Authenticators where possible, unless you have chosen to implement FIDO2 Keys or PassKeys (Discussed below). Many Mobile Authenticator apps now allow you to recover/restore your OTP codes to a new device, which makes them much more user friendly and easy to use.

FIDO2 Keys:
What are FIDO2 Keys? FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online) keys are physical security devices that support passwordless authentication. They can connect to a device through USB, NFC, or Bluetooth. There are many manufacturers for FIDO2 keys, YubiKey’s are one of the most popular FIDO2 keys on the market.
How do FIDO2 keys work? When prompted to authenticate to your web browser/application, insert your FIDO2 key into the USB port or tap it to your NFC reader. Many FIDO2 keys will require you type in a PIN that you setup on the key as well as physically touch something on the key to prove you are at the key and not remote. Once you enter your PIN and touch the key, encryption certificates are unlocked on the physical device and they are confirmed to be valid, you are then signed into the website. Think of this as your own personal ‘lock’ that you see in your browser next to a website, but instead of confirming that the website is secure, the website is confirming that it is talking to you and not someone pretending to be you.
What are good use cases for FIDO2 keys? High-security environments, corporate access, and anyone seeking strong two-factor authentication (2FA) or passwordless access. If you have the means to have a FIDO2 key and your website/application supports it, we strongly suggest you use FIDO2 keys where possible.
What are the downsides of FIDO2 keys? FIDO2 keys cost money, although the price of these keys are coming down quite a bit. You can get keys for under $20 now. You also must keep track of the key, most people will store these in a safe place or keep them on their car key ring. Another downside is that not all websites and services support FIDO2 keys yet, you may be required to use one of the other mentioned options.
FIDO2 keys provided the highest level of phishing resistant MFA. It is strongly recommended to utilize FIDO2 keys where possible. These keys require the physical device, a PIN for the device and proof you are physically at the device, resulting in the highest form of protection from phishing. Additionally, FIDO2 requires the device to be connected to the local computer, it cannot be accessed remotely, this prevents some forms of phishing attacks where attackers trick you into logging into a website on their remote computer, without you even realizing it.
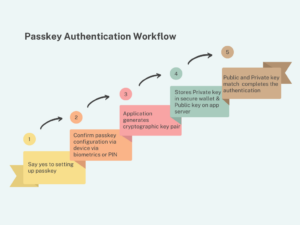
PassKeys:
What are PassKeys? PassKeys are a newer form of authentication designed to work across devices and platforms, supported by initiatives like the FIDO Alliance and W3C. They aim to replace passwords by using a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key stored securely on the user’s device and a public key stored on the server.
How do PassKeys Work? When you set up a PassKey, you authenticate once using another method (like a PIN or biometric), and the PassKey is created. To log in, you proves they have the private key through a simple gesture, like a fingerprint or facial recognition, without the key ever leaving your device. This is very similar to how FIDO2 keys work, but these are tied to your mobile device.
What are good use cases for PassKeys? Universal login experiences across different websites and applications, intended for use on both personal and public devices.
What are downsides of PassKeys? PassKeys are still new, not all sites and services support them yet. In addition, they are tied to your mobile device. If you do not have recovery methods setup, regaining access to your PassKeys could be problematic and difficult.
PassKeys are quickly being adopted industry wide. The largest of tech companies have put their support behind PassKeys, this will be a technology that will be utilized as an industry standard. Implementing PassKeys is strongly suggested over SMS OTP, Authenticator Apps and Magic Links, where possible.
Final Thoughts:
As we navigate the evolving landscape of digital security, the shift towards passwordless authentication represents a pivotal step forward. By embracing these technologies, consumers can enjoy a more streamlined and secure digital experience, free from the hassles of traditional passwords. From Magic Links to FIDO2 Keys and PassKeys, the options are varied, each with its unique advantages and considerations. As the digital world continues to evolve, so too will the methods we use to secure our online identities. Embracing passwordless authentication is not just about enhancing convenience but is a proactive measure to fortify security in our increasingly interconnected lives. Stay tuned for our upcoming exploration of passwordless authentication in enterprise settings, where we’ll delve into the complexities and solutions tailored to organizational needs.